
 Type 2 DM
Type 2 DM
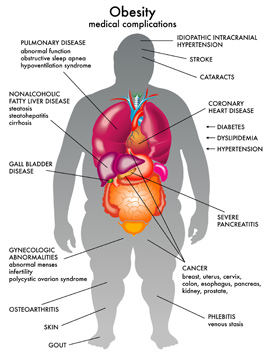
The two most important factors for the development of Type 2 diabetes are increased weight and the genetic tendency. The genetic trait may manifest as having first degree relatives with Type 2 diabetes, though this is not a necessity. Type 2 diabetes is one of a number of complications of obesity.
Complications of Obesity:
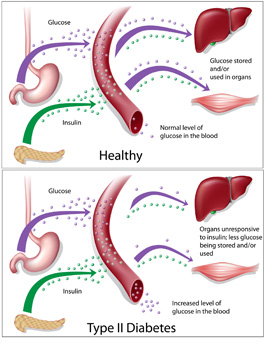
When Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed, the main problem is “insulin resistance”. This means that the person is making insulin (often in very high amounts), but that the body does not respond to it as well as it should. As a result the insulin can’t do its usual job of keeping sugar/glucose stored in organs such as the liver and muscle. The final result of this is that some glucose remains in the blood stream at a higher level than normal causing diabetes.
 Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes:
Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes:
How does someone feel with Type 2 Diabetes?
Unlike Type 1 diabetes, when people have very definite symptoms over a relatively short period of time, people with Type 2 often have very few symptoms when they are diagnosed. This is because Type 2 diabetes tends to come on much more gradually, and on average people have Type 2 diabetes for over 5 years when they are diagnosed.
Other people may present with a complication as the first sign they have diabetes. Because of this is it important to consider getting checked for Type 2 diabetes if you have risk factors (see Table 1 below).
The test for Type 2 diabetes is based on a fasting blood test or sometimes a glucose tolerance test – a fasting blood test followed by a sugary drink followed by a 2nd best test 2 hours later. Most cases can be diagnosed without the need for the oral glucose tolerance test.
Risk factors for Type 2 diabetes
One of the biggest problems with Type 2 diabetes is that high blood sugar levels combine with the frequently also present high blood pressure and cholesterol levels to cause hardening of blood vessel walls. This results in them becoming narrower and increase risk of heart attack and stroke. This process is called atherosclerosis.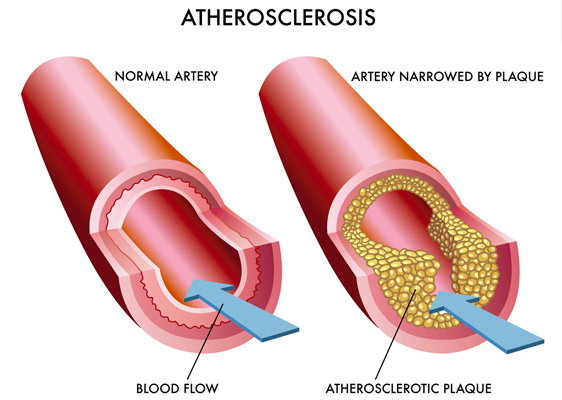
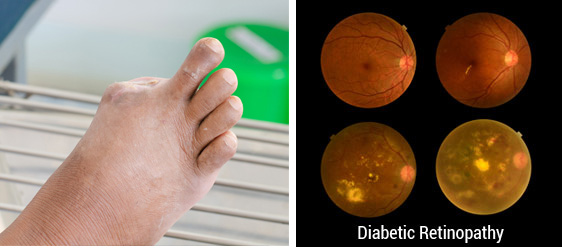
Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness and dialysis in the Western World. Worldwide someone loses a limb from diabetes every 30 seconds.
Diabetes can lead to toe amputation and damage to back of eyes.
The mainstay of treatment is dietary adjustment and increased exercise. Carbohydrates are the glucose-containing part of the diet which contains sugar. We all need carbohydrates but in people with Type 2 diabetes, avoidance of simple (eg sugar, sweets etc) carbohydrates and appropriate quantities of complex (eg brown bread, porridge etc) carbohydrates is the general approach. The necessary dietary adjustments are greater for some people than others and dietician input is usually necessary.

 Sugar is hidden in many foodstuffs and an awareness of carbohydrate content of what is being eaten is very important.
Sugar is hidden in many foodstuffs and an awareness of carbohydrate content of what is being eaten is very important.
It is recommended that 30 minutes exercise a day is required to maintain weight and 60 minutes a day to loose weight. The reality is that any amount of exercise is helpful - from a structured programme in a gym to a simple walk. It is important that the exercise is sufficiently intense in order to gain maximum benefit.
Any form of exercise is beneficial:

A simple device such as a pedometer (or smart phone) can help quantify how active someone is being.

The majority of people with type 2 diabetes will need to go onto medications. Because the condition is progressive – i.e. as time goes on it gets worse in terms of rising blood sugar levels – unfortunately higher doses and more medications are needed as time goes on. Most people will also need tablets for blood pressure and cholesterol too, so unless a lot of weight can be lost at diagnosis with dietary and exercise changes, the medication list for individuals with type 2 diabetes can be relatively long.
Medication load in Type 2 diabetes:
On a positive note, we have many types of medications for type 2 diabetes, some of which can increase the chance of losing weight. Choice of which diabetes treatment is best for a particular person is a very individualised decision and requires a full discussion of the pros and cons of each drug.